SIGMA: Refining Large Language Model Reasoning via Sibling-Guided Monte Carlo Augmentation, a research paper from the AI research team of the Hangzhou International Innovation Institute of Beihang University (H3I), was recently published at the top international academic conference on AI, NeurIPS, showcasing an original breakthrough made by the university's young researchers in basic AI research. Ren Yanwei, a doctoral student admitted in 2024 to the School of Artificial Intelligence at Beihang University, is the first author, while Professor Liu Liu from the Artificial Intelligence Innovation Center (AIIC) at H3I is the corresponding author. The research was jointly carried out by the School of Artificial Intelligence and H3I in collaboration with domestic and foreign research institutions such as Nanyang Technological University, University of Leicester, and the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), demonstrating Beihang University's open cooperation and international influence in AI research.
As large models evolve, merely expanding the data scale is no longer sufficient to significantly improve performance, and the optimization of their reasoning capability has become a new research focus. The SIGMA (Sibling Guided Monte Carlo Augmentation) framework proposed by Ren Yanwei and other researchers innovatively reuses the "sibling nodes" overlooked by conventional Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). By comparing and analyzing the relative merits of different inference paths, the framework provided models with semantic "feedback signals". The mechanism enables models, much like humans, to continually self-correct and refine themselves by comparing different approaches, significantly enhancing logicality and robustness.
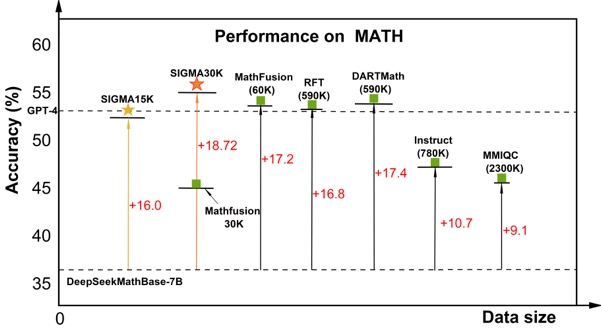
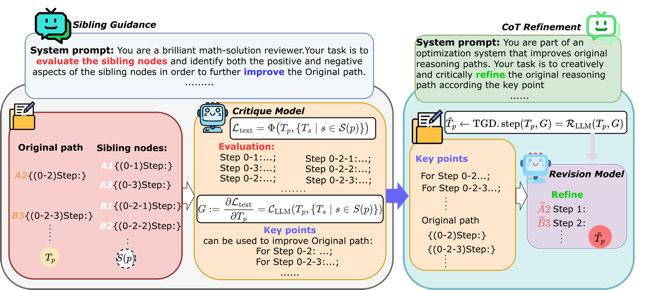
Figure: Experimental results and workflow diagram
Unlike the previous practice of keeping only the outcome of a single path, SIGMA uses a new method called "Textual Gradient Descent" to express the model's reflection process in natural language. As a result, refinement of inference no longer relies on numerical gradients, but on language understanding and semantic feedback. This approach markedly improves inference accuracy and data utilization efficiency, without incurring additional computation. Experiments show that SIGMA can achieve an accuracy of 54.92% on difficult mathematical inference benchmarks, such as MATH, with only 30,000 training samples, surpassing models trained with nearly 600,000 samples. According to studies, high-quality structured utilization of data can deliver a "quality over quantity" advantage in large-model reasoning. In multiple tests, SIGMA achieved leading results on mainstream models, such as DeepSeekMath-7B, LLaMA3-8B, and Mistral-7B, demonstrating strong generality and cross-model adaptability.
The introduction of SIGMA marks another successful integration of basic theory and engineering innovation by Beihang's AI team, demonstrating the university's sustained investment in the training of internationally competitive young researchers and its strength in translating research findings into real-world impact. Looking ahead, the team will continue to explore the interpretability, inference optimization, and self-supervised learning mechanisms of large language models, transitioning AI from "simply being bigger" to "truly being smarter" and from "merely answering questions" to "genuinely reasoning".
Approved by Dong Zhuoning, Zhang Wei, Xu Ran
Edited by Yuan Xiaohui

